Cucurbitaceae family is a diverse family of flowering plants that includes popular vegetables and fruits such as cucumbers, melons, pumpkins, and squash. With over 975 species spread across 98 genera, the Cucurbitaceae family is known for its economic and agricultural significance.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the Cucurbitaceae family, exploring its characteristics, diversity, uses, and cultivation practices.
The Cucurbitaceae family, also known as the gourd family, comprises around 975 species, including cucumber, melon, watermelon, pumpkin, and squash. They are mostly found in tropical and subtropical regions, but some species are adapted to temperate regions.
The Cucurbitaceae Family: A Closer Look

Get ready to explore the fascinating world of the Cucurbitaceae family! From pumpkins to cucumbers, gourds to melons, this plant family has something for everyone. Join us as we take a closer look at these incredible plants, discovering their unique shapes, flavors, and secrets along the way.
Get ready to be amazed by the wonders of the Cucurbitaceae family!
Members of the Cucurbitaceae Family and their Genus
Here is the table of Members of the Cucurbitaceae Family and their Genus.
| Genus | Members |
| Cucurbita | Pumpkin, Squash, Zucchini, Butternut Squash |
| Lagenaria | Bottle Gourd, Calabash Gourd |
| Cucumis | Cucumber, Melon |
| Citrullus | Watermelon, Cantaloupe, Honeydew Melon |
| Momordica | Bitter Gourd, Snake Gourd, Ivy Gourd |
| Benincasa | Wax Gourd, Ash Gourd |
| Coccinia | Ivy Gourd, Scarlet Gourd |
| Sechium | Chayote |
| Cyclanthera | Caigua, Achocha |
| Praecitrullus | Desert Gourd |
| Ibervillea | Buffalo Gourd |
| Trichosanthes | Snake Gourd |
| Cucurbitella | Cucurbitella |
| Sicana | Sicana |
| Hodgsonia | Hodgsonia |
| Gurania | Gurania |
| Kedrostis | Kedrostis |
| Melothria | Melothria |
| Peponopsis | Peponopsis |
| Sicyos | Sicyos |
The Cucurbitaceae family consists of several genera, each containing different members of gourd plants. The table above provides a list of some common genera and the corresponding gourd species within each genus.
Classification of the Family
The Cucurbitaceae family’s classification is based on morphological characteristics such as the fruit type, size, and shape, flower type, and the number of stamens present in the flowers. The fruits are typically elongated or rounded with a thick covering, called a pericarp.
Taxonomy and Classification
The Cucurbitaceae family belongs to the plant order Cucurbitales and is classified within the kingdom Plantae. It is further divided into several subfamilies, including Cucurbitoideae, Zanonioideae, and Cucumerinoideae.
The family exhibits a wide range of morphological and genetic diversity, making it a fascinating subject of study for botanists.
Morphological Features
Cucurbitaceae plants are characterized by their vining or trailing growth habit, usually with tendrils for support. The leaves are typically large and palmately lobed, with a rough texture.
The flowers are unisexual, with separate male and female flowers borne on the same plant. Most species produce edible fruits that are botanically classified as berries, although they can vary significantly in size, shape, and color.
The Cucurbitaceae family has a fascinating origin that spans several continents and millions of years. Let’s explore the evolutionary history and geographical origins of this plant family:
What is the Origin of the Cucurbitaceae Family?
The origin of the Cucurbitaceae family is a complex and dynamic story that involves multiple continents and millennia of evolution. Its diverse origins have contributed to the rich variety of cucurbits we enjoy today.
- Evolutionary History: The Cucurbitaceae family belongs to the order Cucurbitales, which includes other plant families like Begoniaceae and Datiscaceae. It is believed to have evolved around 70 to 90 million years ago during the late Cretaceous period.
- Geographical Origins: The exact geographical origin of the Cucurbitaceae family is a subject of ongoing scientific research. However, various studies suggest that its origin can be traced back to tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- African Origin: Africa is considered a primary center of diversity for the Cucurbitaceae family. Fossil records and genetic studies indicate that wild cucurbits, such as bitter gourd and bottle gourd, have their origins in Africa. The continent is believed to be the ancestral home of several important Cucurbitaceae species.
- Asian Influence: Asia also played a significant role in the evolutionary history of the Cucurbitaceae family. Many cultivated cucurbits, including cucumbers, melons, and pumpkins, have their origins in different parts of Asia. These plants were domesticated and cultivated by ancient civilizations in regions such as India, China, and Southeast Asia.
- American Contributions: The Americas have made substantial contributions to the diversity of the Cucurbitaceae family. Several wild cucurbit species, such as the wild squash and wild cucumber, originated in the Americas. Native American cultures have a long history of cultivating and utilizing these plants for food, medicine, and ceremonial purposes.
- Global Dispersal: Over time, the cultivation and trade of Cucurbitaceae crops have led to their global dispersal. Explorers, traders, and colonizers introduced cucurbits to new regions, leading to their widespread cultivation and integration into local cuisines and agricultural practices.
- Continued Evolution: The Cucurbitaceae family continues to evolve, with ongoing natural selection and human-driven processes shaping the characteristics of these plants. Plant breeding programs and genetic research are contributing to the development of improved cultivars with desirable traits, such as disease resistance, higher yield, and enhanced flavor.
Diversity of Cucurbitaceae Family

The Cucurbitaceae family encompasses an extensive array of plants with diverse characteristics. Let’s explore a few more notable members:
- Cucumber (Cucumis sativus): Known for its crisp texture and refreshing flavor, cucumbers are widely consumed as both a raw vegetable and an ingredient in salads and pickles.
- Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus): A popular summertime fruit from the Cucurbitaceae family, watermelons are known for their juicy, sweet flesh. They come in various sizes and are often enjoyed fresh or used in beverages and desserts.
- Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo): Pumpkins are not only a staple of autumnal decorations but also a versatile ingredient in cooking. They can be baked, roasted, or pureed to create delicious dishes like pumpkin pie.
- Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo subsp. pepo): Zucchini, also known as courgette, is a summer squash that is frequently used in both savory and sweet recipes. It’s mild flavor and tender texture make it a versatile ingredient in the kitchen.
- Melon (Cucumis melo): Melons come in various types, including cantaloupe, honeydew, and muskmelon. These sweet and fragrant fruits are often enjoyed fresh or used in fruit salads and desserts.
- Butternut Squash (Cucurbita moschata): Butternut squash is a winter squash known for its sweet, nutty flavor and creamy texture. It is commonly used in soups, stews, and roasted vegetable dishes.
- Bitter Gourd (Momordica charantia): Also known as bitter melon, this vegetable has a unique bitter taste. It is used in various cuisines, especially in Asian cooking, and is believed to have medicinal properties.
- Acorn Squash (Cucurbita pepo var. turbinata): Acorn squash is a winter squash with a distinct acorn-like shape. It has a slightly sweet and nutty flavor and is often roasted, baked, or stuffed.
- Snake Gourd (Trichosanthes cucumerina): Snake gourd is a long, slender vegetable with a mild flavor. It is commonly used in Asian cuisines, particularly in stir-fries, curries, and soups.
- Luffa (Luffa aegyptiaca): Luffa, also known as sponge gourd or loofah, is a vegetable that is commonly used in Asian cooking. When mature, the fibrous interior of the fruit is dried and used as a natural sponge.
These are just a few examples of the diverse vegetables within the Cucurbitaceae family. Each of them brings unique flavors and culinary possibilities, showcasing the richness of this plant family.
What is the Importance of the Cucurbitaceae Family?
The Cucurbitaceae family holds significant importance in various aspects, ranging from agriculture and nutrition to cultural and economic significance.
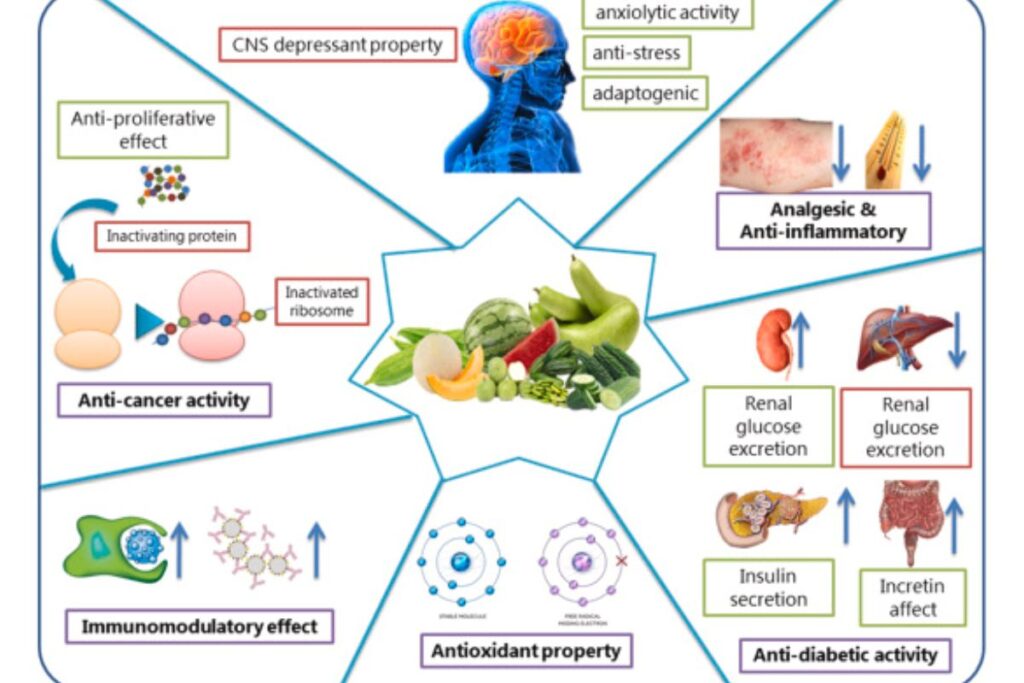
Let’s delve into the key reasons why this plant family is highly valued:
- Nutritional Value: The Cucurbitaceae family offers a diverse range of fruits and vegetables that contribute to a healthy and balanced diet. These plants are often rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. For example, cucumbers are hydrating and contain vitamin K, while watermelons are a good source of vitamin C and lycopene.
- Culinary Versatility: Cucurbitaceae plants provide a wide array of culinary options. From refreshing salads and pickles made with cucumbers to delicious pies and soups created from pumpkins, these vegetables and fruits lend themselves to various preparations and cooking styles.
- Economic Significance: The cultivation and trade of Cucurbitaceae crops have substantial economic implications. Many countries rely on the production and export of cucumbers, melons, and other members of this family for revenue generation and agricultural sustainability.
- Global Food Security: Cucurbitaceae plants play a vital role in ensuring food security worldwide. They are widely grown in both developed and developing countries due to their adaptability to diverse climates. These plants often provide a reliable source of nutrition for populations, particularly in regions where other staple crops may be less accessible.
- Cultural and Traditional Uses: Cucurbitaceae crops hold cultural significance in various societies. They are integral to traditional cuisines and culinary practices across different cultures, contributing to the preservation of cultural heritage and the diversity of culinary traditions.
- Medicinal and Therapeutic Properties: Some members of the Cucurbitaceae family, such as bitter melon and snake gourd, are used in traditional medicine for their potential health benefits. They are believed to possess properties that help regulate blood sugar levels, boost immunity, and aid digestion, among other potential medicinal uses.
- Environmental Benefits: Cucurbitaceae plants contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Their extensive root systems help prevent soil erosion, while their vines provide ground cover, reducing weed growth and conserving moisture in the soil.
- Aesthetic and Ornamental Value: Beyond their practical uses, certain Cucurbitaceae species, like decorative gourds and ornamental pumpkins, are valued for their aesthetic appeal. They are often used in seasonal decorations, enhancing the visual appeal of homes and landscapes.
The importance of the Cucurbitaceae family extends beyond its immediate uses. Its impact on agriculture, nutrition, culture, and the economy underscores its significance in both local and global contexts.
Cultivation of Cucurbitaceae Plants
Cucurbitaceae family plants are cultivated worldwide due to their economic importance and nutritional value. Here are some key aspects of their cultivation:
- Climate and Soil Requirements: Most Cucurbitaceae plants thrive in warm climates with well-drained soil. They require ample sunlight and prefer soil pH levels ranging from 5.8 to 6.8.
- Propagation: Cucurbitaceae plants can be propagated from seeds, which are typically sown directly in the garden or started indoors and transplanted later. Some species can also be propagated through vegetative methods, such as stem cuttings.
- Pest and Disease Management: Cucurbitaceae family plants are susceptible to various pests and diseases, including aphids, cucumber beetles, powdery mildew, and bacterial wilt. Integrated pest management techniques and proper sanitation practices are essential for minimizing damage.
- Harvesting and Storage: The harvesting time for Cucurbitaceae plants varies depending on the species and desired maturity. Fruits are typically harvested when they reach full size and show proper coloration. Proper post-harvest handling and storage conditions are crucial for extending the shelf life of the harvested produce.
What are the Human Health Benefits of Cucurbitaceae Family Vegetables?
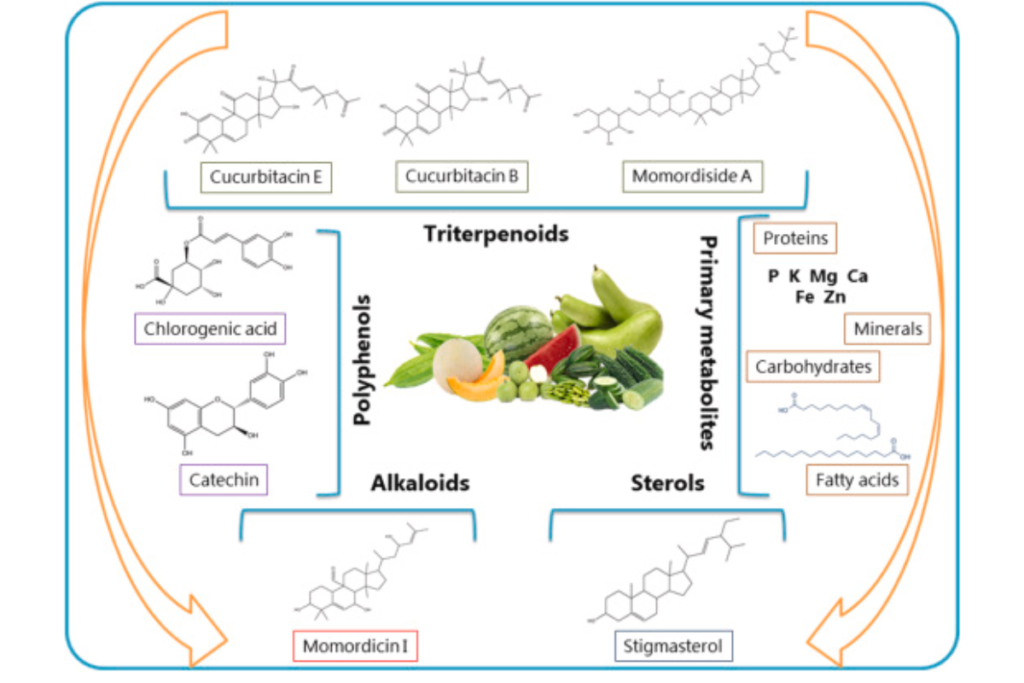
Vegetables from the Cucurbitaceae family not only add delightful flavors and textures to our meals but also offer a range of health benefits. Packed with essential nutrients, these vegetables contribute to our overall well-being and support various aspects of human health.
Let’s explore some of the key health benefits associated with consuming vegetables from the Cucurbitaceae family:
Nutrient-Rich
Cucurbitaceae vegetables, such as cucumbers, pumpkins, and squash, are low in calories and rich in essential nutrients. They are excellent sources of vitamins A, C, and E, as well as minerals like potassium and magnesium. These nutrients support various bodily functions and help maintain optimal health.
Hydration and Digestion
Vegetables like cucumbers and zucchini have high water content, aiding in hydration and promoting healthy digestion. They also contain dietary fiber, which helps regulate bowel movements, prevent constipation, and support a healthy gut microbiome.
Weight Management
Cucurbitaceae vegetables are generally low in calories and high in fiber, making them beneficial for weight management. The high fiber content helps promote feelings of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating and supporting healthy weight loss or maintenance.
Antioxidant Protection
Many vegetables in the Cucurbitaceae family, such as pumpkins and watermelons, are rich in antioxidants. These compounds help protect the body against oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, and support the immune system. Antioxidants also play a role in maintaining healthy skin and combating the effects of aging.
Eye Health
Some Cucurbitaceae vegetables, like pumpkins and butternut squash, are excellent sources of beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining good vision and promoting eye health, including reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Heart Health
The consumption of Cucurbitaceae vegetables can contribute to heart health. These vegetables are generally low in saturated fats and cholesterol and are good sources of dietary fiber, potassium, and antioxidants. These properties help maintain healthy blood pressure levels, reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and promote overall heart health.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Some vegetables from the Cucurbitaceae family, such as cucumbers and bitter melons, contain compounds that exhibit anti-inflammatory properties. These vegetables may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is associated with various chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Hydration and Detoxification
Cucurbitaceae vegetables with high water content, such as cucumbers and watermelons, contribute to proper hydration. Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and supports the functioning of various bodily systems. Additionally, the natural diuretic properties of some cucurbit vegetables can assist in flushing out toxins from the body.
Incorporating a variety of vegetables from the Cucurbitaceae family into our diet can provide us with a range of health benefits. From supporting digestion and hydration to promoting heart health and providing essential nutrients, these vegetables play a valuable role in maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet.
Conclusion
The Cucurbitaceae family is a fascinating group of plants that encompasses a wide range of fruits and vegetables. From the refreshing crunch of cucumbers to the sweet juiciness of watermelons, these plants have become essential ingredients in cuisines worldwide.
Understanding the characteristics, diversity, and cultivation practices associated with the Cucurbitaceae family can help both gardeners and enthusiasts appreciate the significance and versatility of these plants.
FAQs about the Cucurbitaceae Family
Here are some faqs about the Cucurbitaceae family.
Are all members of the Cucurbitaceae family edible?
No, while many members of the family produce edible fruits, some species have toxic or inedible parts. It is important to verify the edibility of each species before consumption.
Are Cucurbitaceae plants difficult to grow?
Cucurbitaceae plants can be relatively easy to grow with proper care and attention. They require suitable environmental conditions, regular watering, and protection from pests and diseases.
Can Cucurbitaceae plants be grown in containers?
Yes, certain Cucurbitaceae species, such as bush varieties of cucumber or small-sized pumpkins, can be successfully grown in containers. Selecting compact cultivars and providing adequate support is essential for container gardening.
Do Cucurbitaceae plants require cross-pollination?
While some Cucurbitaceae species, such as melons, require cross-pollination for fruit development, others, like cucumbers, can self-pollinate. Bees and other pollinators play a vital role in facilitating pollination for many Cucurbitaceae plants.
Can Cucurbitaceae plants be grown organically?
Yes, Cucurbitaceae plants can be grown using organic methods. Organic fertilizers, pest control measures, and crop rotation practices can help promote sustainable cultivation and minimize environmental impacts.
Are there any medicinal uses of Cucurbitaceae plants?
Yes, certain species within the Cucurbitaceae family, such as bitter melon (Momordica charantia), have traditional medicinal uses in various cultures. They are believed to possess anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, and antimicrobial properties.

